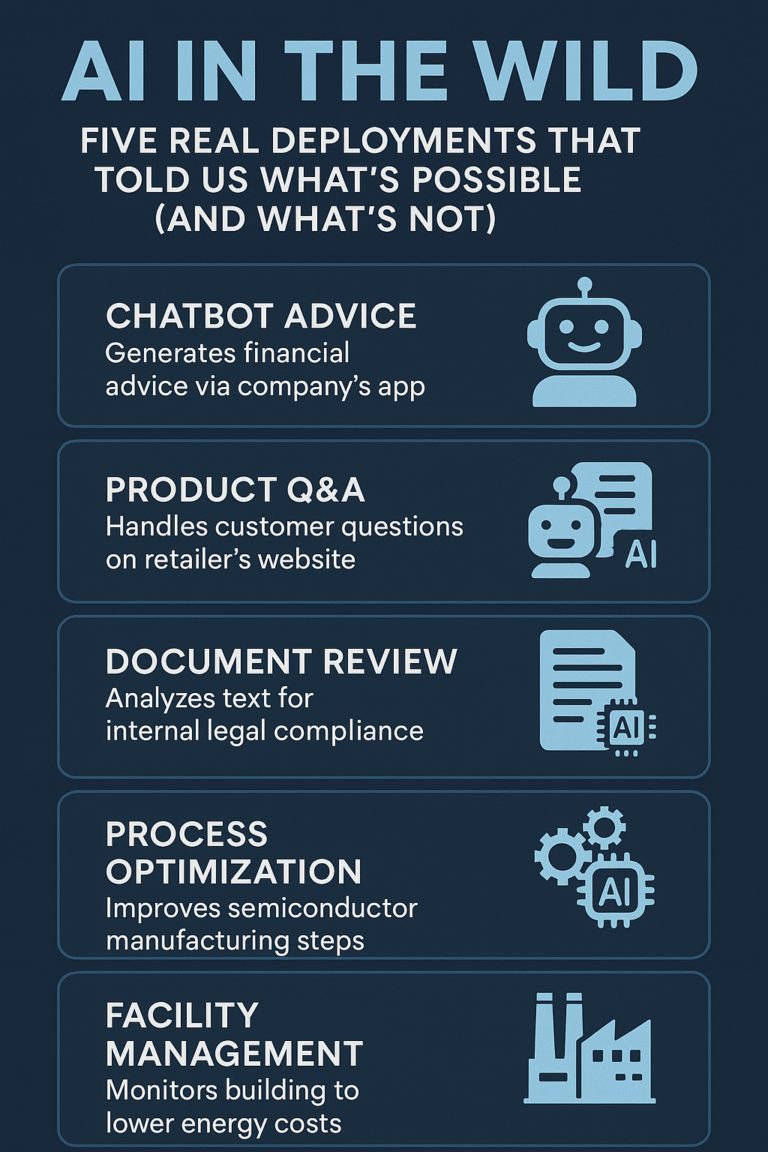
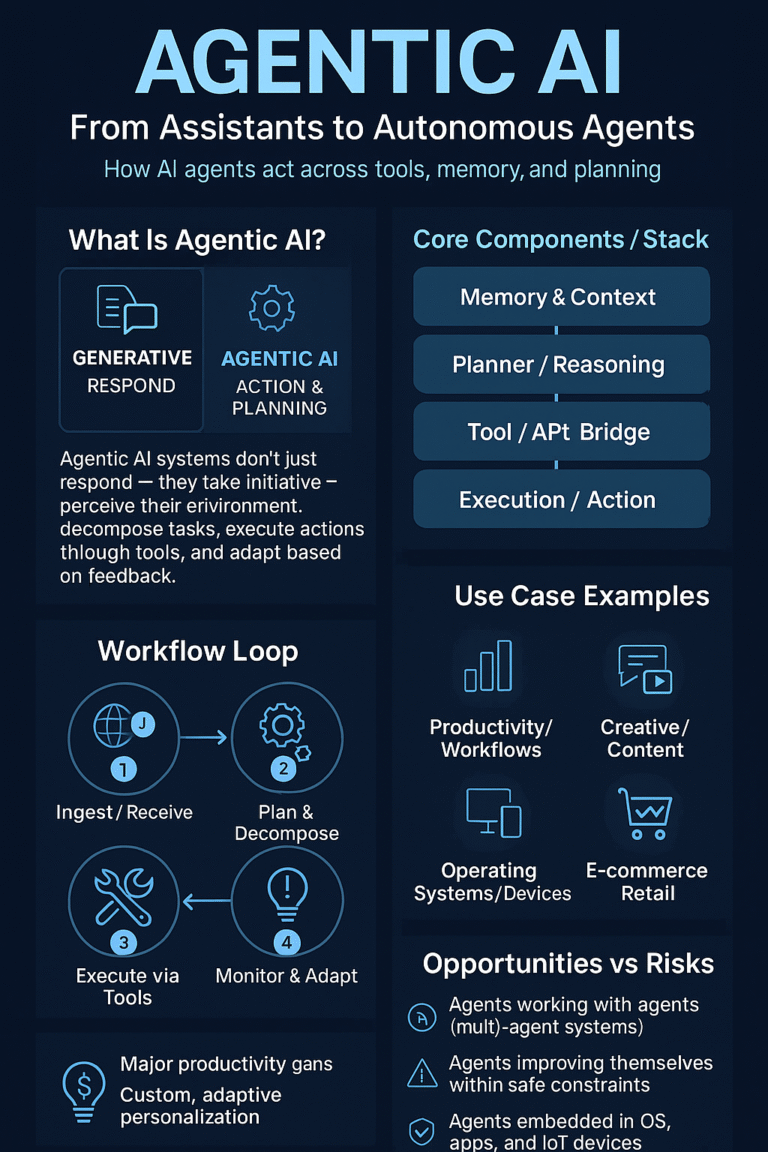
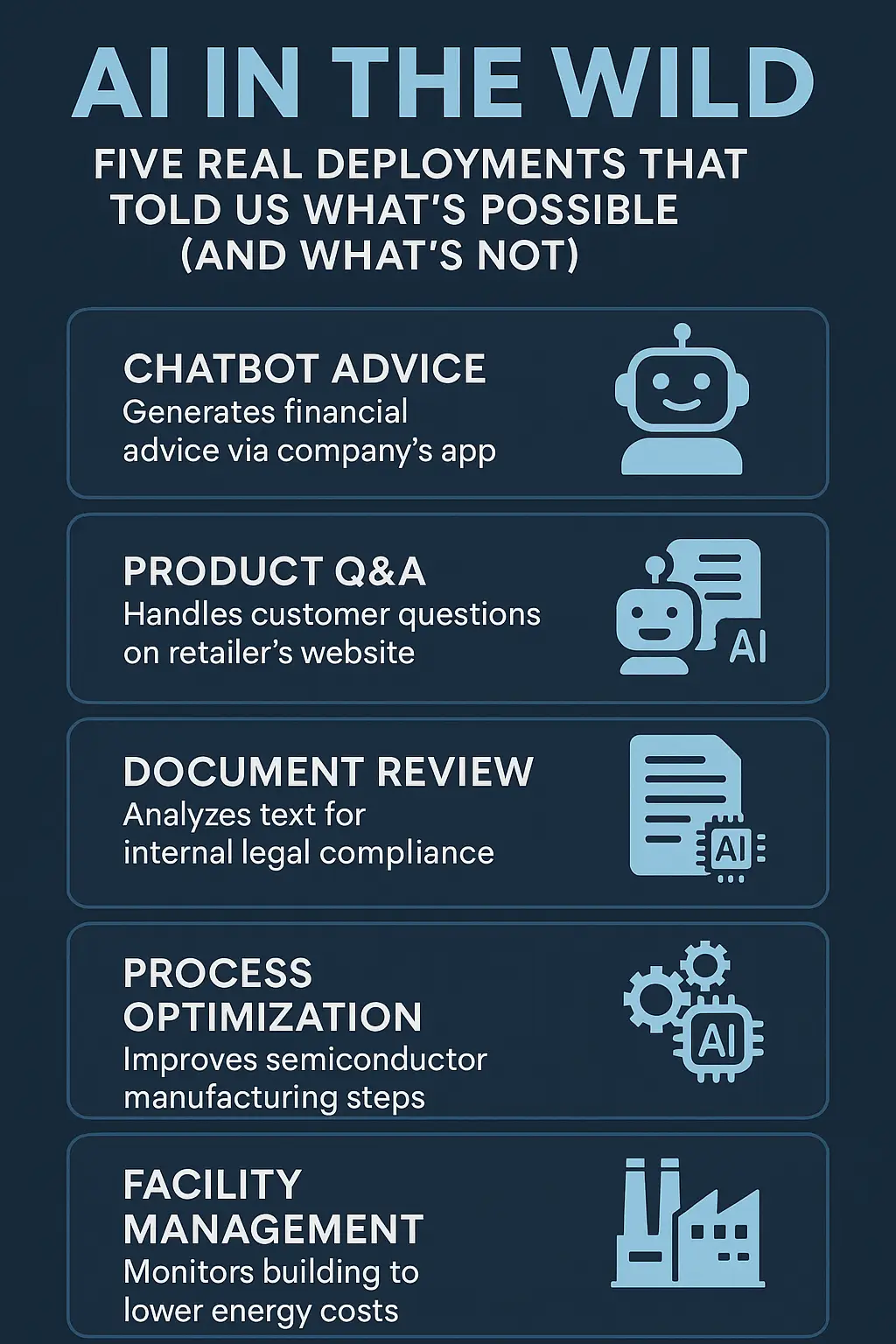
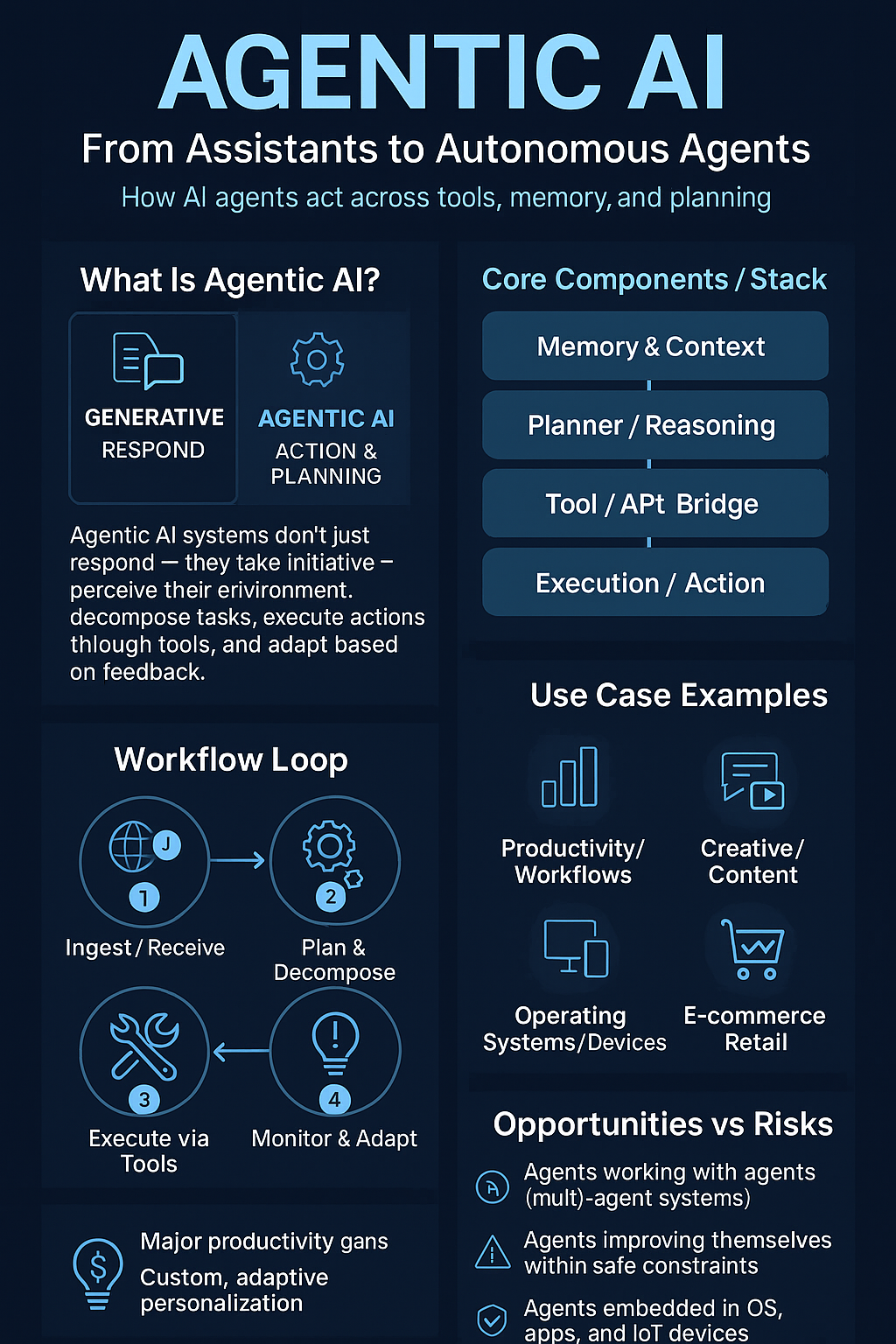
Five Real Deployments That Told Us What’s Possible
Much of AI coverage is speculative or demo-driven — but real-world deployments are harder and far more revealing. In this article, we look at five ambitious AI systems now operating (or in trial) that push boundaries, show failure modes, and point toward where the frontier is headed.
1. Robots That Invent Their Own Tools — Evolution 6.0

Researchers recently unveiled Evolution 6.0, a system that allows a robot to autonomously design and fabricate tools it doesn’t yet have, then use them to complete a task.arXiv For instance, the system might need a lever or hook it has never seen — it generates a 3D model and instructs a tool-creation mechanism, then uses it.
Why it matters: it reduces the human burden of planning out every possible environment or tool.
Caveats: Generalization is still limited — the system struggles when tools must be used in flexible, unpredictable contexts.
2. AR Creation by Voice — ImaginateAR
ImaginateAR is a mobile system enabling users to speak their vision (e.g. “a dragon around a campfire”) and have AI immediately generate 3D AR scenes in situ.arXiv You can refine by voice or gestures, adapt to lighting, and combine with manual edits.
Why it matters: democratizes AR content creation for non-experts, bridging imagination and location-specific overlays.
Challenges: consistency of scale, grounding in physical space, and high demands on compute at mobile scale.
3. AI Traffic Control in Dubai

At GITEX 2025, Dubai unveiled an autonomous AI traffic control system that detects violations in real time — without human input.The Times of India It tracks multiple violation types and feeds analytics back to municipal systems.
Why it matters: an example of city-scale AI operating in unstructured, complex, and safety-critical domains.
Risks: misidentification leads to false tickets; privacy and surveillance concerns; edge-case incidents (e.g. emergency vehicles, pedestrians) must be carefully managed.
4. AI in Operating Systems — Windows 11 Copilot
Microsoft’s recent updates embed Copilot deeper into Windows: voice activation with “Hey, Copilot,” Copilot Vision (interpreting screen content), and Copilot Actions that carry out tasks like placing orders or bookings on behalf of users.Reuters+1
Why it matters: The OS itself becomes a context-aware agent, not just a host for user apps.
Hurdles: Misinterpretation, overreach, latency, privacy. Giving an agent control in a general-purpose OS is risky.
5. The AI Chips Race — OpenAI & Broadcom
The partnership between OpenAI and Broadcom to develop custom AI accelerators marks a shift: AI companies want control over the underlying stack.AP News
Why it matters: Owning the hardware path gives tighter integration — faster inference, optimization, cost control.
Barriers: Massive capital investment, fabrication challenges, supply chain constraints, and competition from incumbents like NVIDIA, AMD, and new entrants (e.g. in China).
Common Patterns, Lessons & Warnings
From these deployments, some themes emerge:
- Edge case fragility: all systems still struggle with surprising inputs.
- Safety first: control loops, human override, validation pipelines are crucial.
- Latency & compute constraints: even powerful models must optimize at the hardware / compilation level.
- Ethics, oversight, and accountability: especially for civic systems (traffic), OS agents, and surveillance.
- Iterative deployment vs grand launches: many succeed via incremental rollouts rather than all-at-once.
Conclusion
These five projects reveal that AI is not a lab toy — it is entering spaces that once seemed reserved for human expertise. But deployment is hard. Success lies in the careful bridging of capability, domain knowledge, safety, oversight, and iteration. As AI continues to seep into everyday systems, these early deployments will be instructive guides — successes to replicate, failures to avoid.